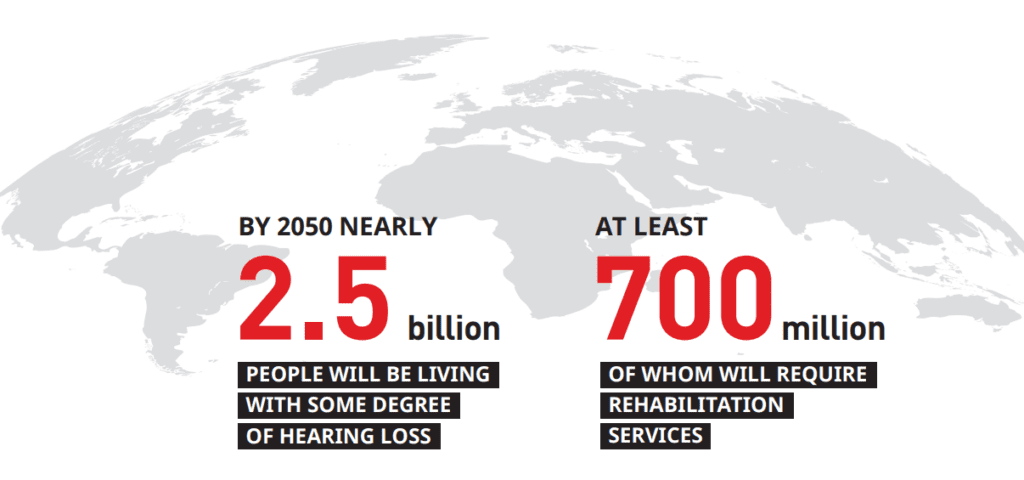
WHO estimates, by 2050 nearly 2.5 billion people will be living with some degree of hearing loss. At least 700 million of whom will require rehabilitation services.
With more than 1 billion young people at risk of avoidable hearing loss. Around 200 million suffer from preventable or treatable chronic ear infections, this gives cause for urgent action.
Nearly 1 trillion dollars are lost annually from unaddressed hearing loss, unless action is taken, this figure will continue to rise in the coming decades. First-ever World report on hearing elaborates on these points and presents an imperative call to action.
Every individual has a unique hearing trajectory according to the genetic characteristics. It s also influenced by biological, behavioral, and environmental factors.
Hearing thresholds greater than 20 dB denote clinical hearing loss. Hearing loss currently affects more than 1.5 billion people worldwide, of whom 430 million have moderate or higher levels of hearing loss.
WHO Report
- More than 360 million people live with disabling hearing loss.
- More than 1 billion people aged 12-35 years are at risk of hearing loss due to recreational noise exposure.
- Globally, the overall cost of not addressing hearing loss is more than $750 billion.
SOLUTIONS ACROSS THE LIFE COURSE
In children, almost 60% of hearing loss is due to causes that can be prevented through immunization, and improved maternal and neonatal care.
Once diagnosed, early intervention is the key to successful outcomes. Medical and surgical treatment can cure most ear diseases
HEARING LOSS ( 2019-2050)
The number of people with hearing loss may increase more than 1.5-fold during the next three decades, with over
700 million likely to experience a moderate or higher level of hearing loss. Unless action is taken, this outcome will almost certainly result in a proportionate rise in associated costs.

The gap in the health system
Perhaps the most glaring gap in health system capacity is in human resources. The gap is consistently high in all parts of the world, ranging from 77% to 83% across WHO regions. And from 74% to 90% across income levels.
Such challenges can be overcome through strategic government-led planning and prioritization processes.









